What is Patch Management?
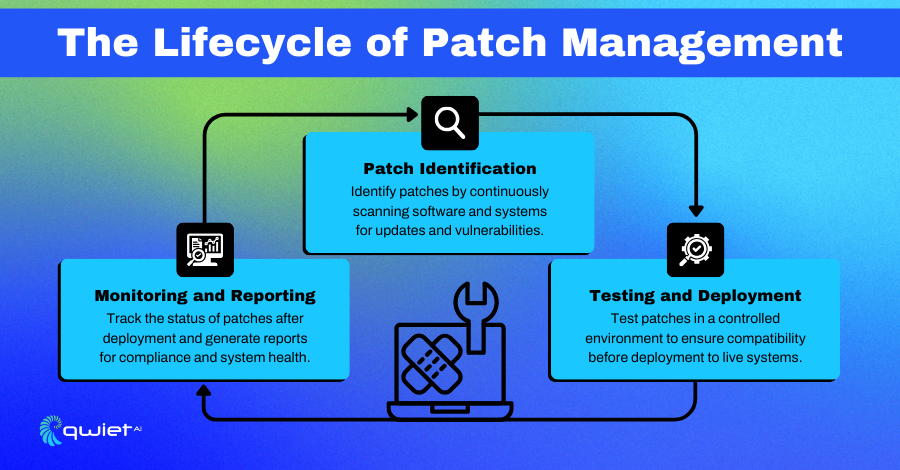
Patch management is the systematic practice of identifying, testing, and applying updates, commonly known as patches, to software components. These patches can target operating systems, applications, or firmware and are often released to fix vulnerabilities, resolve bugs, or optimize performance. The patching process starts with scanning and inventorying all systems to identify missing updates.
From there, these updates are tested to verify compatibility with the current environment before they are deployed across live systems. Given the constant evolution of software and emerging threats, this continuous process requires vigilance.
Patch management aims to improve security, maintain operational stability, and align with industry regulations. Regular patching minimizes the risk of attackers exploiting vulnerabilities while also keeping systems running efficiently without interruptions. It also helps meet compliance standards that mandate up-to-date software for data protection and security practices.
Why Patch Management Matters
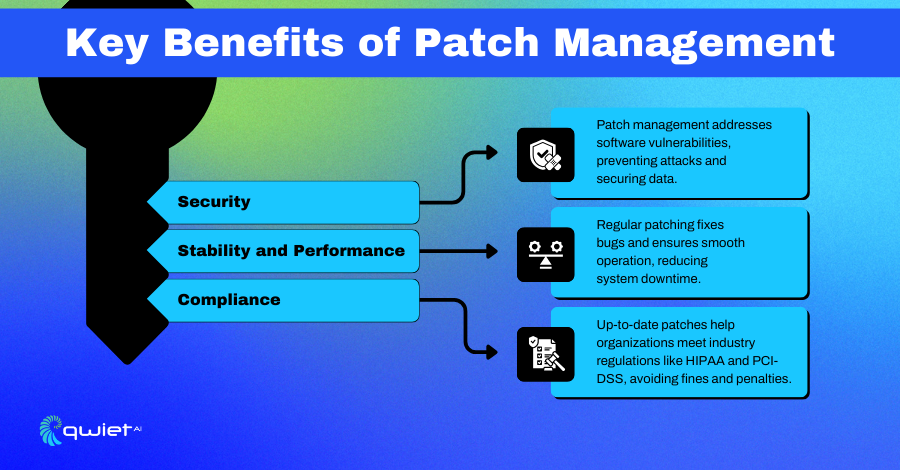
Security
When security vulnerabilities are discovered, malicious actors often weaponize them quickly. Software vendors release patches designed to close these gaps before they can be exploited. Without timely patching, systems remain exposed to attacks like ransomware, data theft, or unauthorized access. By applying security patches promptly, organizations reduce their attack surface and strengthen their defense against potential breaches.
Stability & Performance
Software bugs and performance issues can significantly disrupt operations, from minor glitches to complete system outages. Patches often include bug fixes that address known issues, such as memory leaks, crashes, or performance bottlenecks.
Regular patching improves system stability by reducing unexpected downtime and ensuring that applications perform as intended. For IT teams, this means less time troubleshooting or responding to emergency issues and more time focused on strategic improvements.
Compliance
Many industries, such as healthcare and finance, are governed by strict data security and privacy regulations. Regulations like HIPAA and PCI-DSS often specify that systems must be regularly patched to remain compliant.
Keeping up with updates can lead to audits, fines, or reputational damage. Keeping systems patched aligns with these regulations and contributes to the overall security strategy, reducing the risk of legal consequences and improving audit readiness.
Components of Patch Management
Patch Identification
The first step in patch management is consistently identifying new patches across all systems and software in your environment. This requires regularly scanning all systems, applications, and devices for updates. Whether for operating systems, applications, or even firmware updates, having a system in place to scan and notify when new patches are available automatically helps streamline the process and minimizes the risk of missing critical updates.
It’s important to have a tool or service that can automatically keep track of various vendor releases and updates across multiple platforms. Manually tracking patches for every piece of software is time-consuming and increases the chance that important updates might be overlooked. Automating the identification process ensures that the right patches are found quickly and flagged for further action, making it easier for IT teams to stay on top of all updates.
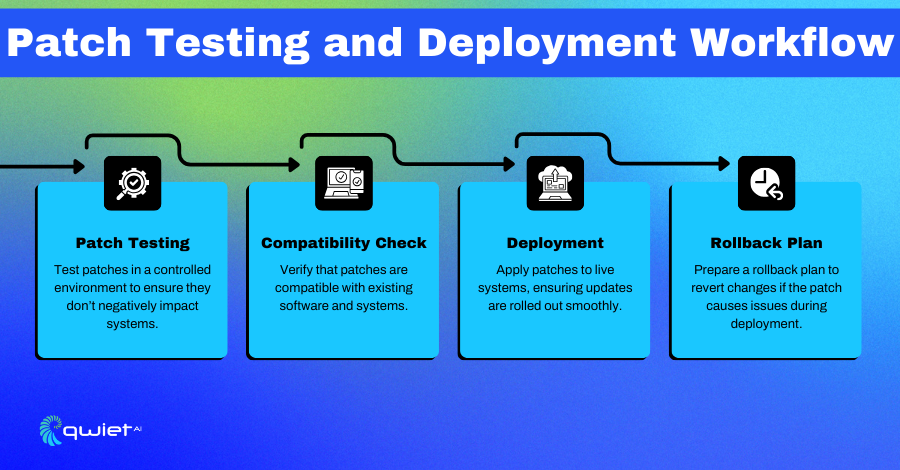
Testing and Deployment
Once a patch has been identified, the next step is testing it in a controlled environment. Applying patches directly to production systems without testing can lead to unintended side effects, such as compatibility issues or conflicts with other applications.
Testing allows you to verify that the patch won’t cause problems before deployment. A dedicated test environment, which closely mirrors the production setup, helps to simulate how the patch will behave, ensuring that it won’t introduce new issues.
After testing, deployment involves rolling the patch out to live systems. Depending on the patch’s importance, this might be done in phases, starting with a few non-critical systems and gradually extending to more crucial parts of the infrastructure. This gradual deployment approach allows teams to monitor for potential issues before fully implementing the patch across all systems, reducing the risk of widespread disruptions.
Monitoring and Reporting
Once patches have been deployed, it is important to track the results to confirm that everything went smoothly. Monitoring tools should be in place to verify that patches were successfully applied to all intended systems, with alerts for any systems where patching may have failed. Ongoing monitoring also helps to ensure that patches continue to work as expected and don’t degrade performance over time.
Generating reports is equally important, particularly for industries where compliance is a factor. These reports document which patches were applied when deployed and to which systems. Such reporting helps organizations meet regulatory requirements and demonstrate that they stay up-to-date with security best practices. It also provides a clear picture of patch management effectiveness, which can be helpful during audits or security assessments.
Conclusion
Patch management is crucial for maintaining secure, stable, and compliant systems by identifying, testing, and deploying patches, along with ongoing monitoring and reporting. A well-executed patching strategy reduces risks from vulnerabilities and improves performance. However, addressing security earlier in the development process is just as important. Qwiet helps identify potential security issues in code before they become larger problems. Book a call with the Qwiet team today to strengthen your security practices.
Read Next
No related posts.
About Qwiet AI
Qwiet AI empowers developers and AppSec teams to dramatically reduce risk by quickly finding and fixing the vulnerabilities most likely to reach their applications and ignoring reported vulnerabilities that pose little risk. Industry-leading accuracy allows developers to focus on security fixes that matter and improve code velocity while enabling AppSec engineers to shift security left.
A unified code security platform, Qwiet AI scans for attack context across custom code, APIs, OSS, containers, internal microservices, and first-party business logic by combining results of the company’s and Intelligent Software Composition Analysis (SCA). Using its unique graph database that combines code attributes and analyzes actual attack paths based on real application architecture, Qwiet AI then provides detailed guidance on risk remediation within existing development workflows and tooling. Teams that use Qwiet AI ship more secure code, faster. Backed by SYN Ventures, Bain Capital Ventures, Blackstone, Mayfield, Thomvest Ventures, and SineWave Ventures, Qwiet AI is based in Santa Clara, California. For information, visit: https://qwietdev.wpengine.com
