Introduction
A Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) is like a detailed list of all your software’s components, licenses, and dependencies. It helps you see exactly what’s in your software and manage potential risks more effectively. As cybersecurity threats grow and regulations tighten in the U.S., SBOM compliance is becoming a top priority. From government mandates like Executive Order 14028 to industry-specific rules, businesses are asked to improve their software’s transparency and accountability. Understanding how SBOMs work and how they fit into compliance efforts is key to staying secure and ahead of regulations.
What is an SBOM?
Definition and Components
An SBOM, or Software Bill of Materials, is like a detailed ingredient list for software. It tells you exactly what’s inside, making managing risks easier and improving transparency across the software supply chain.
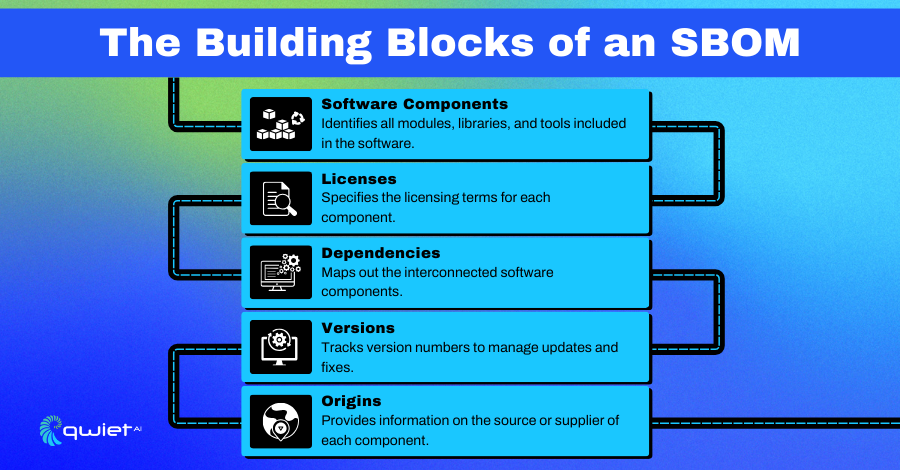
Components of an SBOM:
- Software Components: Lists all the modules, libraries, and tools that are part of the software.
- Licenses: Details the licensing terms for each component.
- Dependencies: Maps out how the software’s components are connected.
- Versions: Tracks version numbers to keep updates and fixes organized.
- Origins: Provides details on where each component came from, like the source or supplier.
Tracking versions and origins in an SBOM helps teams stay on top of updates, patches, and potential vulnerabilities. Version details make spotting outdated or insecure components easier, while origin information clarifies where each piece came from, improving trust and accountability in the software’s supply chain.
Role in Software Transparency and Security
SBOMs make software more transparent and secure by giving you a complete picture of what’s inside. They highlight dependencies, licensing details, and potential vulnerabilities so you can quickly address risks. An SBOM makes fixing issues, complying with regulations, and building trust with clients and partners easier. It’s all about visibility to keep your software safe and reliable.
Why is SBOM Compliance Critical?
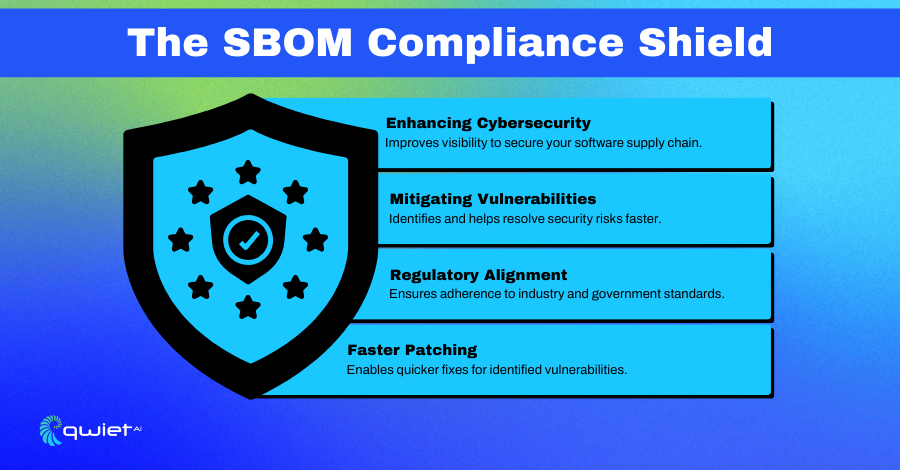
Enhancing Cybersecurity Resilience
SBOM compliance plays a significant role in strengthening cybersecurity by helping organizations proactively manage risks. It allows teams to identify vulnerable components within their software stack and patch them before they become a threat.
With a clear view of dependencies and their associated risks, organizations can react faster to vulnerabilities, reducing the chances of exploitation and minimizing potential damage.
Regulatory and Legal Drivers
Government initiatives like Executive Order 14028 highlight the growing importance of SBOM compliance for improving supply chain security. This order mandates using SBOMs in federal software contracts, setting a clear expectation for transparency and accountability.
Many industries, such as healthcare and finance, also have their strict compliance requirements that now include SBOMs. Meeting these regulations isn’t just about staying compliant—it’s about maintaining trust and avoiding legal or financial penalties.
Benefits of SBOM Compliance
Strengthened Cybersecurity Posture
SBOM compliance helps organizations maintain a stronger defense against cybersecurity threats. Identifying vulnerabilities, addressing outdated libraries, and reducing potential attack surfaces becomes easier by providing visibility into software components and dependencies. This approach to managing risks enhances the overall security of the software environment.
Improved Supply Chain Transparency
With an SBOM, organizations gain better insight into their software supply chain. Knowing exactly what components are in use, where they come from, and how they interact provides clarity and reduces uncertainty. This level of transparency makes it easier to manage risks, track changes, and hold suppliers accountable for their contributions to the software.
Enhanced Trust with Clients and Partners
SBOM compliance signals a commitment to security and transparency, which can build confidence with clients, partners, and regulators. When stakeholders have access to a clear and reliable SBOM, they’re more likely to trust the integrity of the software and its ability to meet their expectations for safety and reliability.
Streamlined Compliance with Other Regulatory Frameworks
Adopting SBOM compliance simplifies meeting requirements across multiple regulatory frameworks. Many standards, such as ISO 27001, NIST, and industry-specific guidelines, overlap in their demand for software transparency and risk management. With an SBOM, organizations can align their practices more efficiently, reducing the complexity of meeting diverse compliance obligations.
U.S. Regulatory Framework Around SBOM
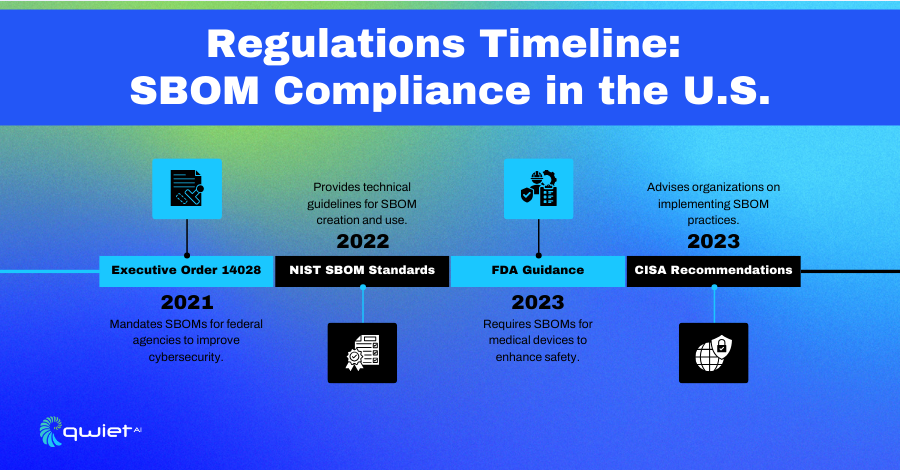
Executive Order on Improving the Nation’s Cybersecurity
The Executive Order on Improving the Nation’s Cybersecurity has brought SBOMs to the forefront of federal cybersecurity initiatives. It highlights the need for SBOMs to improve software supply chain transparency and security. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) plays a key role in defining SBOM standards, working with industry leaders to establish guidelines for creating and managing SBOMs. These standards serve as a foundation for compliance, helping organizations align their practices with federal cybersecurity objectives.
Cybersecurity Guidelines from Federal Agencies
Federal agencies like the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) promote SBOM adoption as part of broader security measures to protect critical infrastructure. CISA has issued guidance to encourage using SBOMs to identify and mitigate software vulnerabilities. In addition, the FDA has outlined requirements for medical device manufacturers to include SBOMs as part of their premarket submissions, emphasizing the importance of transparency in healthcare-related software.
Implications for Federal Contractors and Suppliers
For federal contractors and suppliers, SBOM compliance is no longer optional. The U.S. government requires vendors to provide SBOMs to demonstrate supply chain security as part of their procurement processes.
Please meet these requirements to maintain contract eligibility, particularly for those working with sensitive or high-security projects. These regulations set clear expectations for suppliers to deliver secure, transparent software components to federal agencies.
Challenges of SBOM Compliance
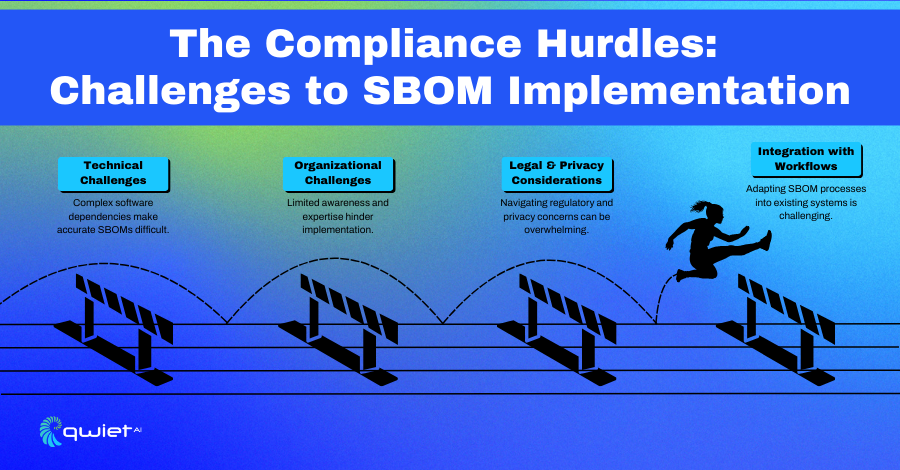
Technical Challenges
SBOM compliance comes with technical hurdles, especially in managing complex software dependencies. Modern software often relies on deeply nested components, which can be difficult to trace and document accurately. Without the right tools and processes, it’s challenging to generate SBOMs that are accurate and complete. Gaps in data or errors in dependency mapping can undermine the effectiveness of SBOMs, leaving organizations vulnerable to security and compliance risks.
Organizational Challenges
Many organizations need more awareness and expertise in adopting SBOM compliance. Teams may need to fully understand the purpose or requirements of SBOMs, making it harder to implement effective practices. Integrating SBOM workflows into existing development processes can also be challenging, particularly for organizations with established pipelines or limited resources. This lack of alignment can create inefficiencies and make compliance feel like an additional burden.
Legal and Privacy Considerations
SBOM compliance must also account for legal and privacy concerns. Sharing detailed information about software components, especially in supply chains, can expose organizations to risks around intellectual property, licensing disputes, or regulatory breaches. Balancing transparency with protecting sensitive information requires careful planning and coordination, particularly when working with external vendors or partners.
Best Practices for Achieving SBOM Compliance
Implementing Automated Tools for SBOM Generation
Automated tools are a practical way to simplify SBOM generation and improve accuracy. Popular tools like SPDX and CycloneDX are widely used to create detailed, machine-readable SBOMs that align with industry standards. Dependency checkers and scanners can also integrate into development pipelines to automatically identify and document components and vulnerabilities. Using these tools helps teams keep up with the complexity of modern software ecosystems without adding unnecessary manual effort.
Establishing a Robust Process for SBOM Maintenance
Maintaining SBOMs over time is as important as creating them. This means keeping them updated as software components change, vulnerabilities are patched, or dependencies are added. Regular audits of SBOMs help ensure they remain reliable and actionable. A clear, consistent process for updating SBOMs ensures teams can rely on them to provide accurate data for compliance and security purposes.
Aligning with SBOM Standards and Guidelines
Adhering to established SBOM standards like SPDX, CycloneDX, and others is important to compliance. These frameworks provide clear guidelines for creating SBOMs that are widely accepted and interoperable across different tools and systems. Aligning with these standards simplifies audits and regulatory reporting and enhances the usability of SBOMs across the supply chain.
Collaboration with Stakeholders
Collaboration with vendors and developers is key to achieving SBOM compliance. Partnering with stakeholders throughout the supply chain ensures transparency and accountability in sourcing and managing software components. Open communication helps address potential gaps in SBOM data and strengthens trust between all parties. When everyone works together, compliance becomes a shared effort rather than a siloed task.
Conclusion
SBOMs are important for keeping your software supply chain secure and transparent. They help you spot vulnerabilities, manage risks, and easily meet regulatory requirements. With cybersecurity threats on the rise, now is the time to prioritize SBOM compliance. Ready to take the next step? Book a demo with Qwiet SBOM today and see how we can help you improve security and compliance in your software supply chain.
Read Next
Interactive Application Security Testing (IAST) Overview
What is Interactive Application Security Testing (IAST)? Interactive Application Security Testing (IAST) analyzes an application’s security while actively running. Unlike other approaches, it integrates directly with the app, allowing it to spot vulnerabilities as the code executes. This gives more accurate insights than methods that only look at static code or run tests outside the […]
Microservices Security Overview
What is Microservices Security? Microservices security is the comprehensive approach to safeguarding each service within a microservices architecture. In this model, each service functions independently, which creates unique security requirements for each one. To secure these distributed services, microservices security involves methods to protect inter-service communications, secure APIs, and manage access and identity across multiple […]
Vulnerability Assessment Overview
What is a Vulnerability Assessment? A vulnerability assessment is a thorough check-up of your information systems to find any security weaknesses. This involves identifying, classifying, and prioritizing potential vulnerabilities in your computer systems, networks, and communication channels. The goal is to uncover any weak spots that might be targeted by cyber threats so you can […]