Key Takeaways
- Risk-Based Approach: Contextual AI security scoring prioritizes threats based on their actual impact and exploitability.
- Beyond Traditional Scoring: Factors in real-world context, such as attack patterns, business impact, and active exploitation trends.
- Improved Accuracy: Reduces false positives and ensures security teams focus on the most critical threats.
What is Contextual AI Security Scoring?
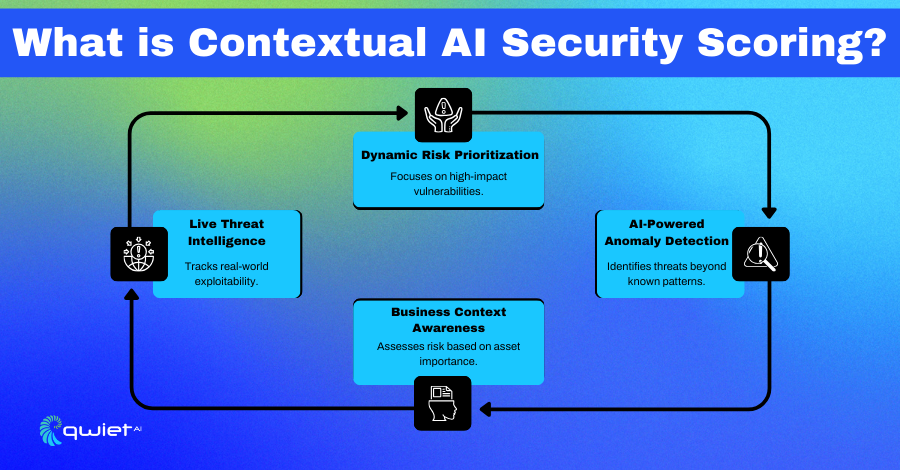
Contextual AI security scoring assesses threats by looking at real-world factors instead of static vulnerability scores. Traditional systems like CVSS assign severity ratings based on predefined criteria. Still, they don’t consider whether a vulnerability is exploited or how much risk it poses in a specific environment.
Contextual AI takes a smarter approach by factoring in live threat intelligence, attack patterns, and business impact to provide a clearer picture of what truly needs attention. This makes security teams more efficient by helping them focus on threats actively used by attackers instead of wasting time on low-risk vulnerabilities. Since risk scores update dynamically as new threats emerge, teams get more accurate assessments and can respond faster to potential issues.
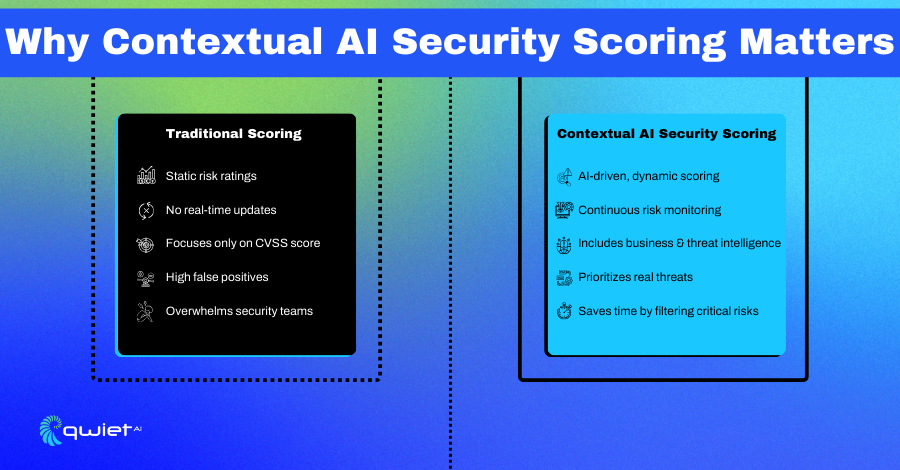
Why Does Contextual AI Security Scoring Matter?
Security
Not every vulnerability is a real threat, and spending time on low-risk issues distracts from what actually matters. Contextual AI security scoring helps security teams prioritize threats that are actively being exploited instead of wasting resources on theoretical risks. Cutting through the noise provides clear, actionable intelligence so teams can focus on vulnerabilities that pose a real danger to their systems and data.
Operational Benefits
Security teams are always juggling multiple priorities, and sorting through endless alerts isn’t the best use of time. Contextual AI security scoring helps by ranking risks based on real-world impact, so teams can spend less time guessing and more time addressing actual threats. It also integrates with security workflows, bringing automation into the mix to streamline decision-making. Within CI/CD pipelines, it gives developers real-time risk insights so security doesn’t slow down development.
Compliance and Governance
Security frameworks like NIST, ISO 27001, and SOC 2 expect organizations to take a risk-based approach to security. Contextual AI security scoring helps meet those standards by providing up-to-date assessments that reflect real-world threats. It also simplifies audits by automatically generating detailed reports on risk assessments. Instead of spending hours manually reviewing security risks, teams have a clear, data-driven approach to staying compliant.
Key Components of Contextual AI Security Scoring
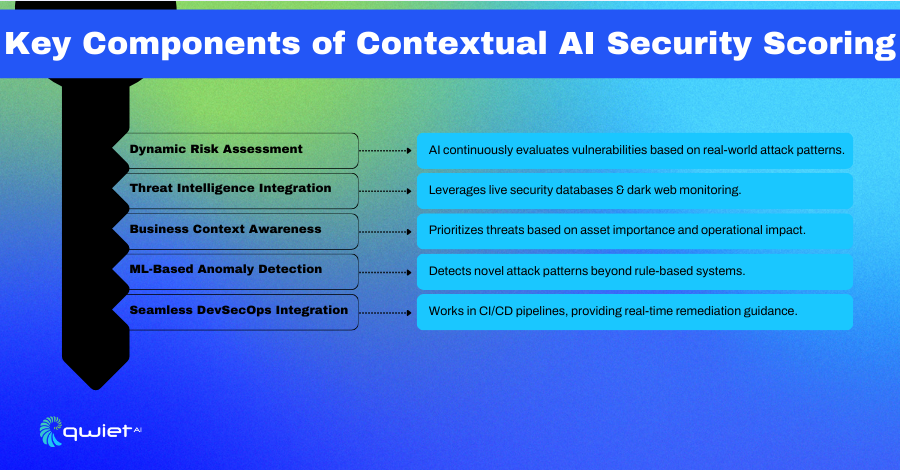
Dynamic Risk Assessment
Not every vulnerability needs immediate attention; some become more dangerous over time. Dynamic risk assessment keeps up with these changes by analyzing real-world exploit trends and attack likelihood. AI continuously updates risk scores based on emerging threats, helping security teams focus on the vulnerabilities actively targeted instead of wasting time on ones that pose little risk.
Threat Intelligence Integration
Knowing that a vulnerability exists isn’t enough. It’s just as important to understand whether attackers use it. Contextual AI security scoring pulls in live threat feeds, MITRE ATT&CK data, and dark web monitoring to analyze attacker behavior. This helps security teams avoid emerging threats by identifying vulnerabilities that are being actively discussed or weaponized.
Business Context Awareness
A vulnerability in a system handling sensitive data is much more concerning than an issue in a less critical system. Business context awareness considers this, prioritizing threats based on their potential impact. Security teams can focus on the vulnerabilities that could lead to real damage rather than treat every issue equally.
Machine Learning-Driven Anomaly Detection
Security threats don’t always follow predictable patterns. Traditional security tools rely on predefined rules, which means they often miss new or evolving attack methods. Machine learning-driven anomaly detection catches unusual activity by recognizing deviations from normal behavior. This helps detect threats that haven’t been seen before, allowing security teams to stop attacks before they escalate.
Seamless DevSecOps Integration
Security should work with development, not against it. Contextual AI security scoring integrates into CI/CD pipelines to automatically assess risks without slowing down. Developers get clear, prioritized remediation guidance so they know exactly what needs to be fixed, reducing back-and-forth between teams and keeping security aligned with development speed.
Conclusion
Traditional vulnerability scoring often misses the mark. It treats every issue the same without considering whether a vulnerability is being exploited or how much risk it poses. This leads to wasted time, unnecessary alerts, and security teams drowning in low-priority issues. Contextual AI security scoring takes a smarter approach. It looks at real-world factors like active attack trends, business impact, and emerging threats to prioritize what matters. This helps teams reduce noise, focus on real risks, and strengthen security without unnecessary delays. It also makes compliance easier by providing accurate, up-to-date risk assessments. Upgrade your security strategy with Contextual AI Security Scoring today by booking a demo with Qwiet today.
FAQ
What is Contextual AI Security Scoring?
It’s a smarter way to assess security risks using real-world threat data. Instead of relying on static vulnerability scores, it looks at factors like active exploit trends, attacker behavior, and business impact to give a more accurate picture of what needs attention.
How does it differ from traditional vulnerability scoring?
Traditional scoring methods, like CVSS, assign fixed severity ratings without considering whether a vulnerability is being exploited. Contextual AI security scoring is dynamic it constantly updates risk levels based on live threat intelligence so teams can focus on the vulnerabilities that pose real, immediate risks.
How does it improve security operations?
It helps security teams cut through the noise by filtering out low-risk vulnerabilities and prioritizing the ones that matter. By reducing false positives and automating risk assessments, teams can spend less time sorting through alerts and more time addressing real threats.
Can it integrate into DevSecOps?
Yes! It works directly within CI/CD pipelines, so security checks happen automatically without slowing development down. Developers get real-time risk assessments and clear guidance on what needs to be fixed, making security a natural part of the workflow.
Read Next
No related posts.
About Qwiet AI
Qwiet AI empowers developers and AppSec teams to dramatically reduce risk by quickly finding and fixing the vulnerabilities most likely to reach their applications and ignoring reported vulnerabilities that pose little risk. Industry-leading accuracy allows developers to focus on security fixes that matter and improve code velocity while enabling AppSec engineers to shift security left.
A unified code security platform, Qwiet AI scans for attack context across custom code, APIs, OSS, containers, internal microservices, and first-party business logic by combining results of the company’s and Intelligent Software Composition Analysis (SCA). Using its unique graph database that combines code attributes and analyzes actual attack paths based on real application architecture, Qwiet AI then provides detailed guidance on risk remediation within existing development workflows and tooling. Teams that use Qwiet AI ship more secure code, faster. Backed by SYN Ventures, Bain Capital Ventures, Blackstone, Mayfield, Thomvest Ventures, and SineWave Ventures, Qwiet AI is based in Santa Clara, California. For information, visit: https://qwietdev.wpengine.com
