Key Takeaways
- Monorepo Security Requires Contextual Analysis: Traditional security tools struggle with monorepos due to their scale and complexity, often missing critical vulnerabilities.
- Code Property Graphs Provide Full Visibility: CPG analysis offers a complete security model, linking code structure, data flow, and dependencies to detect complex attack paths.
- Scalable, AI-Driven Security: Qwiet AI delivers accurate and scalable security analysis for large monorepos, minimizing false positives and prioritizing real threats.
What is AppSec Analysis in a Monorepo?
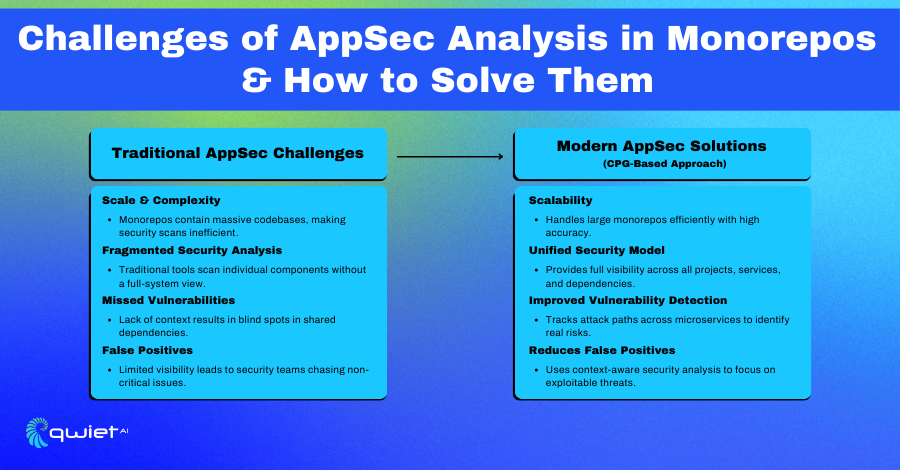
In a mono repo, application security (AppSec) analysis focuses on scanning large, unified codebases that often contain multiple projects, services, and shared libraries. Since all these components live in a single repository, security teams face a unique challenge in identifying vulnerabilities across different services while tracking how they interact. Traditional security approaches aren’t built for this complexity level, making it harder to understand potential risks fully.
As mono repos grow, scaling security analysis becomes difficult. Traditional tools tend to focus on scanning individual components without considering the bigger picture, leaving gaps in visibility. This limited context means they often miss vulnerabilities or flag irrelevant issues, which wastes time and makes security less effective. To properly secure mono repos, organizations need solutions that can analyze code across all services and dependencies while giving security teams meaningful insights into how risks might connect.
Different Approaches to Monorepo Security Analysis
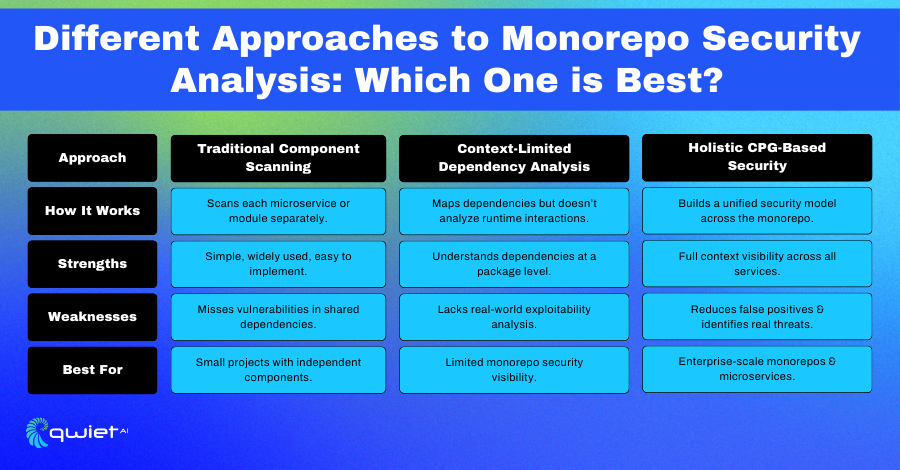
Scanning Individual Components (Traditional Approach)
Traditional security tools scan each service or module separately without analyzing how they interact within the larger mono repo. While this method can catch vulnerabilities in isolated components, it fails to consider the full context.
This leads to significant blind spots, especially in shared libraries or services that rely on one another. Vulnerabilities in inter-service communication and dependency relationships are often missed, increasing overall security risk.
Context-Limited Dependency Analysis
Some tools go further by mapping dependencies between services. While this helps identify vulnerabilities in individual libraries or packages, it doesn’t show how those services behave together at runtime.
As a result, security teams are left with fragmented insights, missing how vulnerabilities could be exploited across multiple components in real-world scenarios.
Holistic Code Property Graph (CPG) Approach
A Code Property Graph (CPG) approach builds a complete security model by connecting code structure, dependencies, and data flow across the entire mono repo. This method provides full context, allowing security teams to detect complex attack paths that traditional tools might overlook.
Analyzing the code holistically reduces false positives and gives teams more accurate insights into which vulnerabilities matter and how they could be exploited.
How Qwiet AI Solves Monorepo Security Challenges
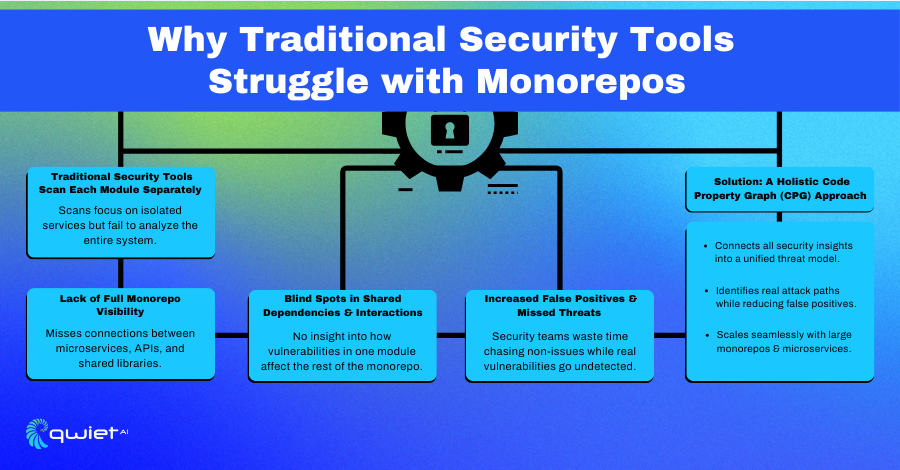
Qwiet AI addresses the complexities of mono repo security through its advanced Code Property Graph (CPG) analysis. This method unifies security data across all projects within a mono repo, creating a comprehensive threat model that links code structures, data flows, and dependencies. By providing this holistic view, Qwiet AI enables security teams to identify vulnerabilities that might be overlooked when analyzing isolated components.
The platform’s end-to-end context awareness is particularly beneficial for tracking vulnerabilities across microservices, APIs, and shared libraries. Qwiet AI can pinpoint complex attack paths and offer precise insights into potential security risks by understanding how these elements interact within the mono repo.
Leveraging machine learning, Qwiet AI detects exploitable security risks while minimizing false positives. This AI-driven approach ensures that security alerts are relevant and actionable, reducing the noise that often hampers effective vulnerability management.
Designed for scalability, Qwiet AI efficiently handles large and complex mono repos without compromising accuracy or speed. This scalability ensures that the platform provides reliable security analysis as your codebase grows, making it a robust solution for organizations managing extensive mono repositories.
Conclusion
Traditional security tools often fall short in monorepos because they lack the context and scalability to analyze large, interconnected codebases. Scanning individual components without understanding how they interact leaves significant blind spots, increasing the risk of missed vulnerabilities. A Code Property Graph (CPG) approach provides the most accurate and scalable way to analyze security across the mono repo, giving teams full visibility and actionable insights into real risks. Ready to experience how this can improve your security strategy? Book a demo today.
FAQ
What is AppSec analysis in a mono repo?
AppSec analysis in a mono repo focuses on scanning and securing large, unified codebases containing multiple projects and services. It aims to identify vulnerabilities in interconnected services, shared libraries, and APIs, which traditional tools often miss due to their limited context.
Why do traditional security tools fail in monorepos?
Traditional security tools are designed for smaller, isolated codebases. In monorepos, they typically scan individual components without understanding how services interact. This leads to incomplete results, missed vulnerabilities, and fragmented security insights.
What is a Code Property Graph (CPG), and how does it improve security?
A Code Property Graph (CPG) is a security model that connects code structure, data flow, and dependencies into a single framework. It allows for a complete security analysis across an entire mono repo, helping to detect complex attack paths and reduce false positives.
How does Qwiet AI help secure monorepos?
Qwiet AI uses CPG-based analysis and machine learning to track vulnerabilities across all services and dependencies within a mono repo. It provides a real-time, end-to-end security context and minimizes noise from false positives, allowing teams to focus on real threats more easily.
Read Next
The Autonomous AppSec Journey
Introduction As AI and automation reshape industries, application security (AppSec) rapidly evolves from systems that support analysts to those that can function independently. This post walks you through the stages of autonomous AppSec, showing how AI-driven systems change how security is managed. You’ll discover how the technology works at each level of automation and what […]
SBOM Compliance Simplified: What U.S. Companies Need to Know
Introduction A Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) is like a detailed list of all your software’s components, licenses, and dependencies. It helps you see exactly what’s in your software and manage potential risks more effectively. As cybersecurity threats grow and regulations tighten in the U.S., SBOM compliance is becoming a top priority. From government mandates […]
The Top 10 AppSec Trends Shaping Cybersecurity in 2025
Key Takeaways Focus on API and Supply Chain Security: Strengthen API security with token-based authentication, API gateways, and AI-powered monitoring. Use AI-enhanced Software Bill of Materials (SBOMs) to identify and prioritize risks in third-party dependencies. Implement Zero-Trust at the Application Layer: Secure APIs, microservices, and data by enforcing strict access controls, continuous verification, and micro-segmentation […]